

A Marketing Information System (MIS) is a management information system designed to support marketing decision-making. It brings together many different kinds of data, people, equipment, and procedures to help an organization make better decisions.
In the ever-evolving world of business, staying ahead of the curve is paramount for survival and growth. The key to this competitive edge lies in a well-structured Marketing Information System (MIS). This blog post will unravel the intricacies of MIS, its components, and its role in transforming business strategies
The role of a company’s marketing information system (mis) is important because it aids in decision-making, marketing research, validating internal records, and most importantly acts as a marketing decision support system.
Contents hideThis section will provide a comprehensive overview of what a Marketing Information System is. We’ll delve into its definition, purpose, and why it’s a game-changer in the modern business landscape.
Definition of Marketing Information System: A Marketing Information System (MIS) is a strategic tool used by businesses to collect, analyze, and present data related to their market environment. It encompasses a structured set of procedures and methods designed to generate, analyze, disseminate, and store anticipated marketing decision information on a regular, continuous basis.
The initial function of a marketing information system is to asses the business landscape and provide recommendations that help in the recommendation of various business processes specifically related to marketing
Purpose: The primary purpose of an MIS is to support the decision-making process within a business. It provides managers with the necessary information to make informed marketing decisions and create effective marketing strategies. The data collected through an MIS can include information about customer demographics, buying habits, sales trends, competitor analysis, and market research.
The initial function of a marketing information system is that It balances the information that a firm wishes to have with the information a firm needs.
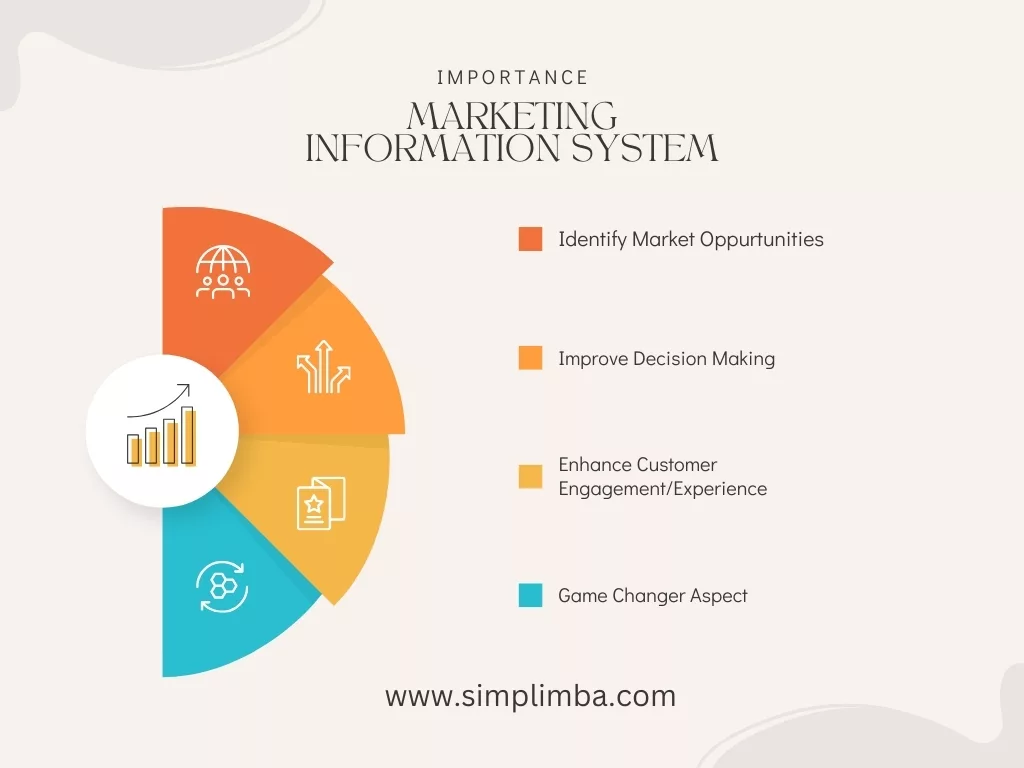
The importance of an MIS lies in its ability to help businesses stay competitive in today’s rapidly changing market environment. It enables businesses to:
Identify Market Opportunities: An MIS can help businesses identify new market opportunities, track market trends, and understand customer needs and preferences. This can lead to the development of new products or services, expansion into new markets, or improvement of existing offerings.
Improve Decision-Making: By providing accurate and timely information, an MIS supports better decision-making at all levels of the organization. This can lead to improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and increased profitability.
Enhance Customer Satisfaction: An MIS can help businesses understand their customers better, leading to improved customer service, personalized marketing efforts, and ultimately, higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Game-Changer Aspect: In the era of big data and digital transformation, an MIS is indeed a game-changer. It allows businesses to harness the power of data and use it to drive strategic decision-making. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that leverage customer behavior data to generate behavioral insights outperform their peers by 85 percent in sales growth and more than 25 percent in gross margin.

Internal Records:
Internal records are the backbone of any Management Information System (MIS). They provide a historical context, allowing decision-makers to analyze past performance and make informed predictions about future trends. This data typically includes sales records, inventory details, financial statements, and other operational data.
See also The Third Person Effect Theory in Mass Communication and 7 Powerful ImpactsThe effectiveness of internal records can be measured using data accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. A formula commonly used to assess data quality is:
Data Quality Score = (Completeness + Accuracy + Timeliness) / 3
High-quality internal records can significantly improve decision-making efficiency and accuracy, leading to better business outcomes.
Marketing Intelligence:
Marketing intelligence refers to the external data that a company gathers about the market in which it operates. It includes information about competitors, market trends, customer behavior, and economic indicators.
An example of a formula used in marketing intelligence is the Market Growth Rate:
Market Growth Rate = (Current Market Size – Previous Market Size) / Previous Market Size * 100%
This formula helps businesses understand the growth potential of their market and make strategic decisions accordingly.
Marketing Research:
Marketing research involves systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of data about issues relating to marketing products and services. It involves conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, and other research methods to gather information about customer needs, preferences, and attitudes.
A commonly used statistic in marketing research is the Confidence Interval, which gives an estimated range of values that is likely to include an unknown population parameter. The width of the confidence interval gives us some idea about how uncertain we are about the unknown parameter.
Confidence Interval = Sample Mean ± (Z-score * Standard Deviation / √Number of Observations)
Marketing Decision Support System (MDSS):
An MDSS is a computerized information system that supports business and organizational decision-making activities. It utilizes data, models, and user-friendly software to support the formulation of marketing strategies.
The effectiveness of an MDSS can be measured using the Decision Quality Metric:
Decision Quality = (Relevance + Reliability + Timeliness + Completeness) / 4
This metric provides a quantitative measure of the quality of the decisions made using the MDSS, with higher scores indicating better decision-making.
Each of these pillars plays a crucial role in the functionality and effectiveness of an MIS. By understanding and optimizing each component, businesses can significantly enhance their decision-making capabilities, drive growth, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
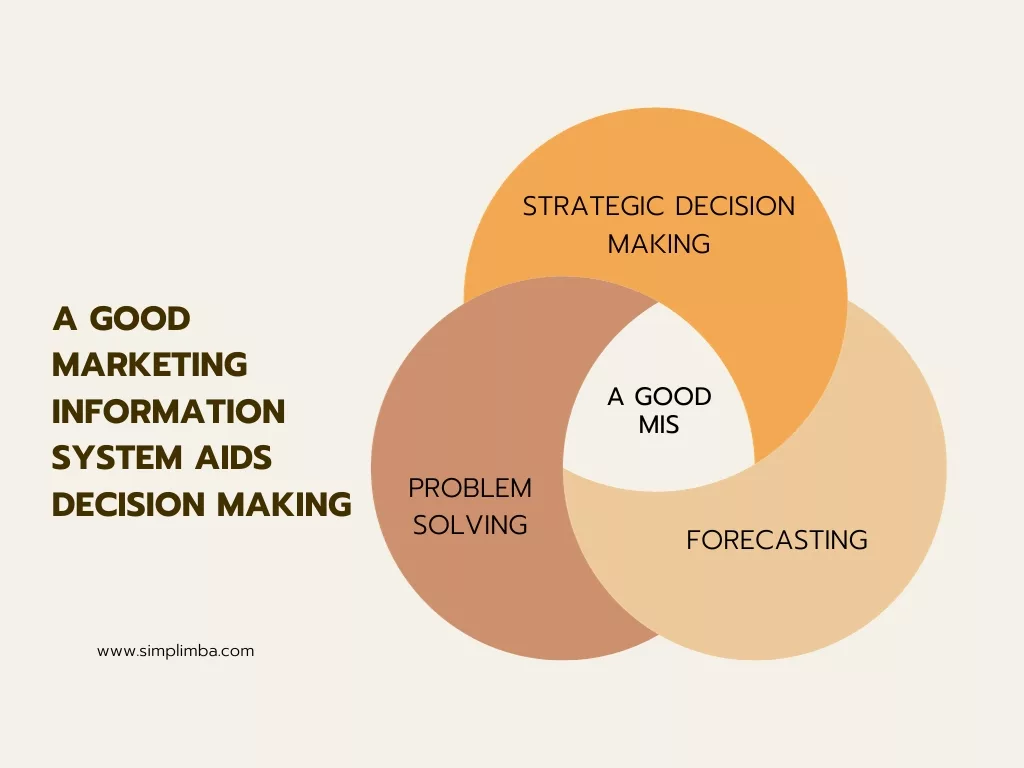
This part will focus on the practical implications of an MIS in a business setting. We’ll explore how it aids in strategic decision-making, forecasting, and problem-solving.
An MIS provides critical data that can be analyzed and used for strategic decision-making. This data can include everything from sales reports to customer behavior data, which can help businesses understand their market and make informed decisions.
For instance, an MIS can help identify trends in sales data that might indicate a need for a new marketing strategy or product development. It can also help identify areas where costs could be reduced without negatively impacting product quality or customer satisfaction.
The MIS can use a formula like the Decision Tree Analysis, which helps to evaluate the potential outcomes of a decision. The formula is as follows:
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) = ∑ (Payoff x Probability)
Here, the payoff is the potential outcome of the decision, and the probability is the chance of that outcome occurring.
An MIS can also be used for forecasting, which is essential for planning and budgeting. It can analyze historical data to predict future trends, helping businesses prepare for what’s to come.
One common forecasting method used is Time Series Analysis. This method uses historical data to identify patterns and trends that can predict future outcomes. The formula for a simple linear regression time series forecast is:
Where Y is the forecasted value, a is the Y-intercept, b is the slope of the trend line, and t is the period.
An MIS can be a valuable tool in problem-solving. It can provide data that helps identify problems, analyze their causes, and evaluate potential solutions.
The MIS can use a variety of problem-solving models, such as the Cause and Effect Diagram, also known as the Fishbone Diagram. This diagram helps to identify, explore, and display the possible causes of a specific problem or quality characteristic.
See also 15 Very Relevant Mixed Branding Examples that transformed businessesTo sum up, an MIS plays a crucial role in decision-making, forecasting, and problem-solving within a business. It provides valuable data that can be analyzed and used to make strategic decisions, predict future trends, and solve problems. It’s an indispensable tool for any business that wants to stay competitive in today’s data-driven marketplace.
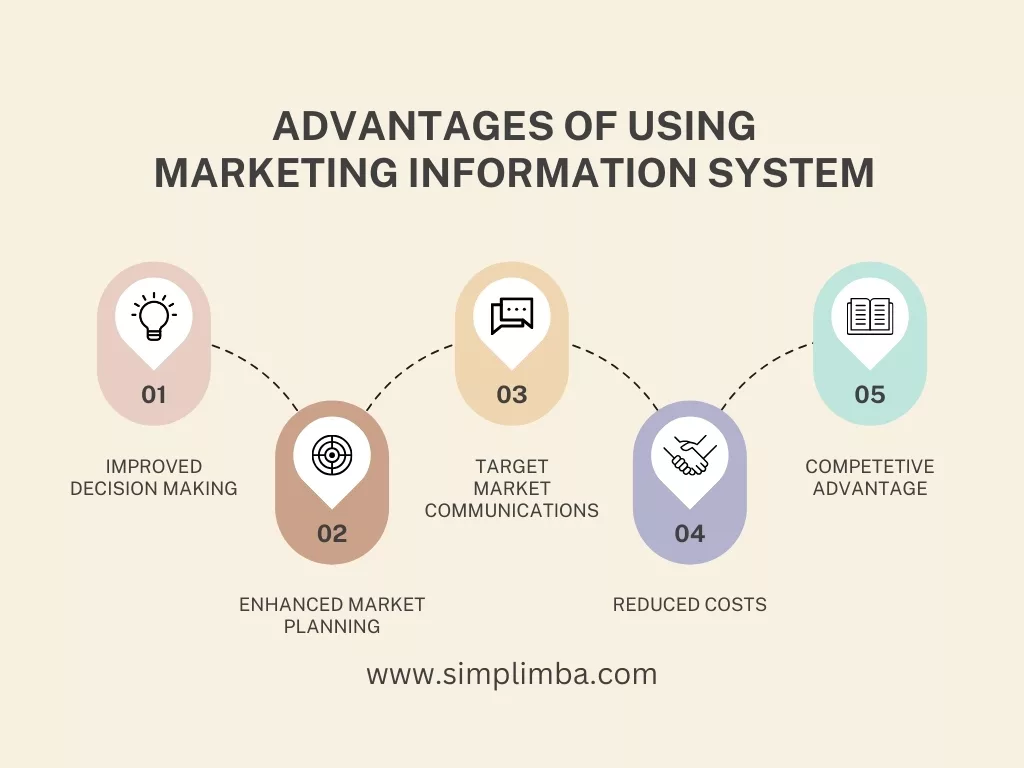
Improved Decision-Making: The primary advantage of using a MIS is that it can significantly improve the decision-making process. With a robust MIS, marketing managers can access real-time, accurate data that allows them to make informed decisions. For example, a survey by Adobe found that 76% of marketers believe measurement and analytics are crucial to their business growth.
Enhanced Marketing Planning: The MIS can help in creating more effective marketing plans. It provides data about customers’ preferences, market trends, and competitors’ strategies, enabling managers to devise more targeted and competitive marketing plans. According to the 2020 CMO Survey, companies that use data-driven marketing have an edge over their competitors, with a 16% to 20% increase in marketing ROI.
Target Market Identification: With a MIS, companies can easily identify their target market. It provides demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral data that can help a business reach its ideal customer. According to a report by McKinsey, businesses that leverage customer behavior data to generate behavioral insights achieve an 85% increase in sales growth and a 25% increase in gross margin.
Reduced Costs: The MIS can also lead to significant cost savings. By automating data collection and analysis, MIS reduces labor costs. Moreover, its ability to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing campaigns can also decrease marketing expenses. An IBM study found that incorporating AI (part of MIS) into marketing can cut costs by as much as 30%.
Competitive Advantage: Lastly, an effective MIS can provide a competitive advantage. It gives marketers insights into the strategies and performances of their competitors, enabling them to adjust their strategies accordingly. According to a Harvard Business Review report, companies using analytics and data (elements of MIS) to inform decision-making are more productive and experience higher returns than their competition.
Transitioning from theory to action, this section will provide a roadmap for businesses looking to implement an MIS. We’ll discuss the stages of implementation, potential challenges, and tips for success.
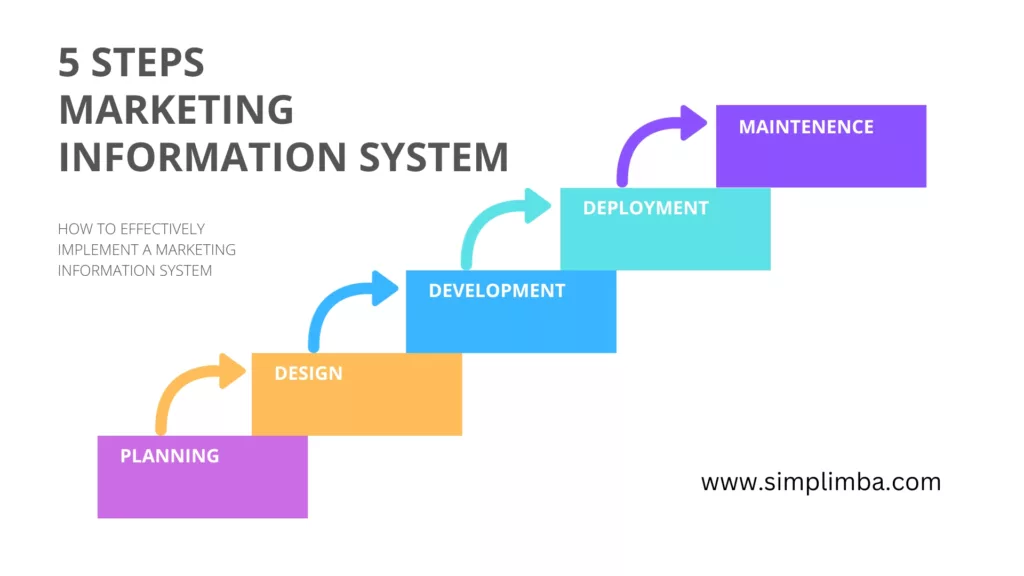
Planning: The first step in implementing an MIS is careful planning. This involves defining the scope of the system, setting goals, and identifying key stakeholders. An effective plan should also include a detailed timeline, budget, and risk management strategy.
Design: Once the plan is in place, the next step is to design the MIS. This involves deciding on the software, hardware, and network infrastructure that will be used. The design phase also includes creating a detailed blueprint of the system’s architecture and user interface.
Development: The development stage involves building the MIS based on the design blueprint. This includes coding, testing, and debugging the system. It’s crucial to ensure the system is user-friendly and meets the organization’s needs.
Deployment: After the MIS has been developed, it’s time to deploy it. This involves installing the system, training users, and transitioning from the old system to the new one.
Maintenance: The final stage of implementation is maintenance. This involves regularly checking the system for errors, making necessary updates, and providing ongoing user support.
Implementing an MIS can be a complex process, and there are several potential challenges to be aware of. These include:
Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to adopting a new system, especially if they are comfortable with the old one.
Technical Difficulties: There may be technical issues during the development and deployment stages, such as software bugs or hardware malfunctions.
See also Needs Wants and Demands in Marketing - Differences, Types and Psychology Behind it: A Comprehensive Overview
Budget Overruns: The cost of implementing an MIS can be high, and it’s not uncommon for projects to go over budget.
Involve Stakeholders: Ensuring that all stakeholders are involved in the planning and design stages can help to ensure the MIS meets everyone’s needs.
Provide Training: Offering comprehensive training can help to overcome resistance to change and ensure users are comfortable with the new system.
Regularly Review and Update: Regularly reviewing and updating the MIS can help to keep it running smoothly and ensure it continues to meet the organization’s needs.
As we gaze into the crystal ball, we’ll discuss the future trends in MIS. This will include the role of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data in shaping the future of MIS.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly revolutionizing the field of Management Information Systems (MIS). AI can automate routine tasks, provide predictive analysis, and improve decision-making processes.
Automation: AI can automate routine tasks, freeing up time for employees to focus on more complex tasks. For example, AI can automate data entry, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Predictive Analysis: AI can analyze large amounts of data to identify trends and patterns. This can help businesses predict future outcomes and make informed decisions. For example, AI can predict customer behavior, helping businesses to tailor their marketing strategies.
Improved Decision-Making: AI can provide insights and recommendations based on data analysis. This can improve the decision-making process, leading to better business outcomes. For example, AI can provide recommendations on how to optimize operations, reduce costs and improve productivity.
Machine Learning (ML), a subset of AI, is also playing a crucial role in the future of MIS. ML can analyze data and learn from it, improving its performance over time.
Data Analysis: ML can analyze large amounts of data to identify trends and patterns. This can help businesses to make informed decisions. For example, ML can analyze customer behavior, helping businesses to tailor their marketing strategies.
Continuous Learning: ML can learn from data, improving its performance over time. This can help businesses to adapt to changing circumstances. For example, ML can learn from customer feedback, helping businesses to improve their products or services.
Predictive Modeling: ML can build predictive models based on data analysis. This can help businesses to predict future outcomes and make informed decisions. For example, ML can predict sales trends, helping businesses to plan their inventory.
Big Data is transforming the field of MIS by providing businesses with access to vast amounts of data. This can improve decision-making processes and provide businesses with a competitive advantage.
Improved Decision-Making: Big Data can provide businesses with access to large amounts of data, improving the decision-making process. For example, Big Data can provide insights into customer behavior, helping businesses to tailor their marketing strategies.
Competitive Advantage: Big Data can provide businesses with a competitive advantage by providing insights that are not available to competitors. For example, Big Data can provide insights into market trends, helping businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
Predictive Analysis: Big Data can analyze large amounts of data to identify trends and patterns. This can help businesses to predict future outcomes and make informed decisions. For example, Big Data can predict customer behavior, helping businesses to tailor their marketing strategies.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page